What is Metadata?
Metadata is information about other data.
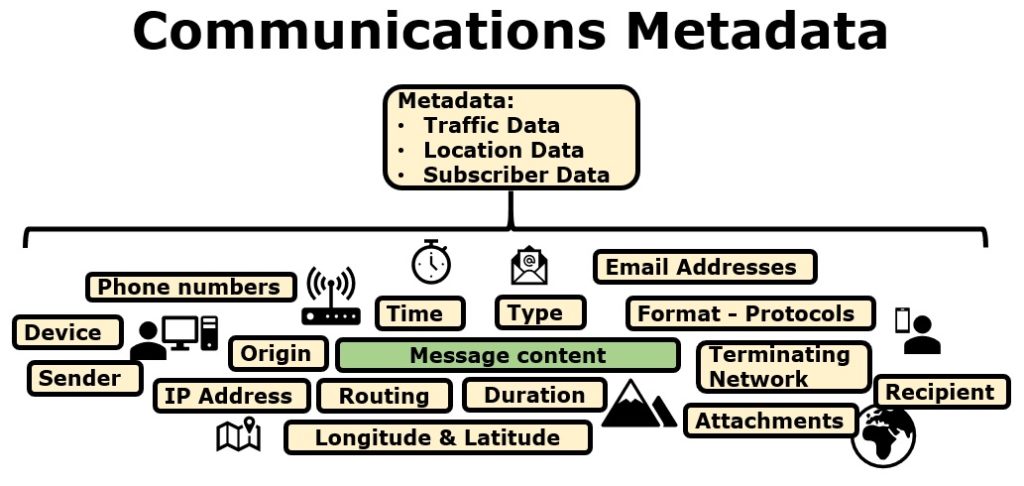
For example, regarding the content of a message, metadata can include traffic data, location data, subscriber data, and specifically they type of data, the time the message was sent and received, device information, sender information, phone numbers, the origin of a message, the IP address, routing information, duration of the message, longitude and latitude, email addresses, protocol format, terminating network information, attachments, and recipient information.
Is metadata personal data subject to the GDPR? Yes. Metadata can be used to identify an individual. Metadata can not only be personal data, but highly sensitive in nature.
“[M]etadata derived from electronic communications may also reveal very sensitive and personal information. These metadata includes the numbers called, the websites visited, geographical location, the time, date and duration when an individual made a call etc., allowing precise conclusions to be drawn regarding the private lives of the persons involved in the electronic communication, such as their social relationships, their habits and activities of everyday life, their interests, tastes etc.” See Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL concerning the respect for private life and the protection of personal data in electronic communications and repealing Directive 2002/58/EC (Regulation on Privacy and Electronic Communications)
